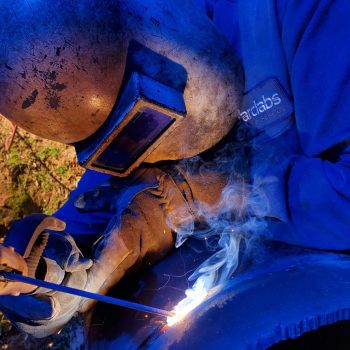
What is Arc Welding
Arc welding is what is known as a fusion welding process. It is one of the most common welding processes and is used extensively in various industries due to the strong, high-quality welds it creates.
Arc Welding in Theory
The arc welding process uses an electrical arc that forms between an electrode and the base metal to generate a temperature of around 6,500 degrees Fahrenheit. This causes the metals to melt where they are to be joined, with the molten metal fusing as it cools and solidifies to create a metallurgical bond between the metals.
Arc Welding in Practice
Arc welding is a process where an electrode welding rod is attached to the welding torch which connects to a portable welding machine. When the power source is turned on, the electrode becomes live. By touching the rod to the base metal, the current will move through the rod and complete the electrical circuit. When the rod is pulled back, the electrical arc required to melt the metal is generated. Rods are often designed to melt during the process to add filler to the weld.
As a welder gains experience, they will begin to understand that there are several factors and techniques that influence the weld, its strength and quality, including the current (AC or DC), the size of the electrode, the length of the arc and the angle of travel.
Industrial Uses
Arc welding is a popular choice because it is used successfully on many different metals, including steel, iron, copper and nickel. The portable equipment used in arc welding has added to its versatility and made it a popular choice in several industrial settings.
Automobile, shipping and aerospace manufacturers all rely on arc welders in their manufacturing processes. Similarly, the construction industry looks to arc welders when constructing buildings, bridges and other steel structures, while the mining, oil and gas and power generation industries also utilize their skills.
Pros and Cons
The equipment used for arc welding is affordable. It is portable, making it easy to transport, and with the arc not affected by wind or temperature, it adapts perfectly to an outdoor environment.
Although the process is simple, arc welding produces an incredibly strong weld that is equally effective on thick metals, creating a final weld with high corrosion resistance. In addition, it is a quick process that often creates time savings compared to other welding techniques.
Despite it being one of the simplest welding processes, it requires time and practice to master the technique and create effective welds. It is also less effective when used on thin and reactive metals such as titanium.
Lastly, arc welding is considered a low-efficiency weld. This means that it produces more waste than some of the other welding processes, leading to increased production costs, especially on big jobs.
The technique discussed is just one of several types of arc welding. If you are interested in finding out more about arc welding, call Arclabs Welding School on 877-647-4111.
More on arc welding
[wpu_silo links=’35’]
 877-647-4111
877-647-4111